World Wide Web
The World Wide Web (WWW), also referred to as the Web, is an information system that makes it possible to access documents and other web resources over the Internet.
DPrograms like web browsers can access documents and other downloadable media that are made available to the network through web servers. Uniform resource locators are character strings that are used to identify and locate servers and resources on the Internet (URLs). A web page formatted in Hypertext Markup Language is the original and still most popular type of document (HTML). This markup language supports simple text, images, video and audio content that has been embedded, as well as scripts (short programmes) that implement complex user interaction. In addition, the HTML language supports embedded URLs (hyperlinks), which offer direct access to other web resources. Following such hyperlinks across various websites is known as web navigation, also known as web surfing. Web pages that serve as application software are known as web applications. The Hypertext Transfer Protocol is used to transfer data from the Web across the Internet (HTTP).
Difference between World Wide Web and Internet
Some people misinterpret the terms “internet” and “World Wide Web.” They misunderstand each other and believe they are the same thing. Internet and WWW are completely different. It is a global network of gadgets, including laptops, tablets, and computers. It allows users to chat online and send emails to other users. You use the internet, for instance, when you send an email or engage in online chat.
However, you are using the World Wide Web—a network of servers accessible via the internet—when you access a website like cshub.in to gather information. A browser on your computer requests a webpage, which the server then renders for your browser. Your computer is referred to as a client, which executes a programme (a web browser) and requests information from another computer (a server).
History of World Wide Web
It is a project that Timothy Berner Lee started in 1989 to help researchers at CERN collaborate effectively. is a group called the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), which was created for the advancement of the internet. Tim Berners-Lee, also known as the father of the web, is in charge of this organisation.
How the Invention Started
Tim Berners-Lee took the initiative to create the World Wide Web in March 1989 by penning the initial proposal. In May 1990, he wrote a second proposal. After a few months, in November 1990, it was formally formulated as a management proposal with Robert Cailliau. The key ideas and terminology relating to the Web were outlined in this proposal. The World Wide Web, a “hypertext project” that allowed browsers to view a web of hypertext documents, was described in this document. The three primary technologies were included in his proposal (HTML, URL, and HTTP).
Tim Berners-Lee was able to test his theories in 1990 by running the first Web server and browser at CERN. He wrote a note on his NeXT computer, which he used to create the code for his Web server: “He is a server machine. Do Not Turn It Off!” so that someone does not unintentionally turn it off.
The Web Grows
A small number of users had access to the NeXT computer platform. Later, work began on creating a “line-mode” browser that could function on any platform. A “line-mode” browser, Web server software, and a library for developers were all part of Berners-WWW Lee’s software when it was first released in 1991.
It was accessible to coworkers using CERN computers in March 1991. In August 1991, after a few months, he released the WWW software on internet newsgroups, sparking interest in the project all over the world. Tim Berners-Lee first unveiled a graphic user interface for the internet on August 6, 1991. On August 23, 1991, it became accessible to all.
Hypertext Markup Language (HTML)

A common markup language used to create web pages is HTML. Through the use of HTML tags or elements, it describes the structure of web pages. These tags are employed to classify various types of content, including headings, paragraphs, tables, images, and more. When you open a webpage, you won’t see any HTML tags because browsers only use them to render a web page’s content, not to display them. HTML is used to display text, images, and other resources through a Web browser, to put it simply.
Web Browser

A web browser, which is commonly known as a browser, is a program that displays text, data, pictures, videos, animation, and more. It provides a software interface that allows you to click hyperlinked resources on the World Wide Web. When you double click the Browser icon installed on your computer to launch it, you get connected to the World Wide Web and can search Google or type a URL into the address bar.
In the beginning, browsers were used only for browsing due to their limited potential. Today, they are more advanced; along with browsing you can use them for e-mailing, transferring multimedia files, using social media sites, and participating in online discussion groups and more. Some of the commonly used browsers include Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Internet Explorer, Safari, and more.
Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP)
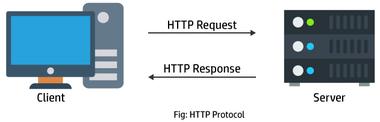
An application layer protocol called Hyper Text Transfer Protocol (HTTP) makes it possible for the World Wide Web to function efficiently. It is built on the client-server architecture. The web server that hosts the website is contacted by the client, a web browser. This protocol specifies the message formatting and transmission requirements as well as the responses that the web server and browser should provide to various commands. An HTTP command is sent to the Web server when a URL is entered in the browser, and it then transmits the requested Web Page.
A connection to the web server is established when we use a browser to open a website, and the browser then interacts with the server by sending an HTTP request. In order to communicate with the server, HTTP is used over TCP/IP. After processing the browser’s request and sending a reply, the server cuts off the connection. As a result, the browser gets the user’s content from the server.
Working of WWW
The Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP), Web browsers, and other technologies form the foundation of the World Wide Web (HTTP).
To access web pages, use a web browser. Programs that display text, data, pictures, animation, and video on the Internet are referred to as web browsers. Web browsers’ software interfaces can be used to access World Wide Web resources that are hyperlinked. Web browsers were initially only used for browsing the Internet, but they are now more commonly used. Searches, mailing, file transfers, and many other activities can all be done using web browsers. Google Chrome, mozilla firefox and Internet Explorer are a few of the most popular browsers.
Features of WWW
- HyperText Information System
- Distributed
- Open Standards and Open Source
- Cross-Platform
- “Web 2.0”
- Dynamic, Interactive and Evolving.
Difference between the Internet and WWW?
The internet is a global network of interconnected computers, while the World Wide Web (WWW) is a system of information that is accessed via the internet. The internet provides the infrastructure for various services like email, file transfers, and online chatting, while the WWW is a collection of web pages formatted in HTML and accessed through web browsers. Essentially, the internet is the hardware that connects devices, and the WWW is the software that allows users to navigate and interact with content online.

